Coefficient of Thermal Expansion Data
A Coefficient of Thermal Expansion, typically represented by the symbolWithin small temperature changes, the change in the length of a material is proportional to its change in temperature. Materials expand as temperatures increase, and contract with decreasing temperatures. Different materials expand by different amounts as shown in the table below.
The data shows thermal expansion material properties that correspond with an approximate temperature of 20 degrees Centigrade (68 degrees Fahrenheit). A material's Thermal Expansion Coefficient is not a fixed constant... the Coefficient value itself also increases (slightly) with higher temperatures.
All data should be considered as approximate as values can vary widely between individual material specimens depending on several factors including alloy type and heat treatment.
|
Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
(Coefficient of Expansion data for selected materials - listed from smallest-to-largest value) |
|||||||||||
| Metal or Alloy
Group Classification |
Material Designation | Coefficient of Expansion
|
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion Relative Value |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
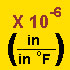 |
||||||||||
| Pure Metals | Tungsten | 4.5 | 2.5 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Molybdenum | 4.8 | 2.7 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Chromium | 4.9 | 2.7 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Zirconium | 5.7 | 3.2 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Rhenium | 6.2 | 3.4 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Tantalum | 6.3 | 3.6 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Iridium | 6.4 | 3.6 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Ruthenium | 6.4 | 3.6 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Rhodium | 8.2 | 4.6 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Vanadium | 8.4 | 4.7 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Titanium | 8.6 | 4.8 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Platinum | 8.8 | 4.9 | ||||||||
| Iron Alloys | Steel (1.45% C) | 10.1 | 5.6 | ||||||||
| Iron Alloys | Gray Cast Iron | 10.5 | 5.8 | ||||||||
| Iron Alloys | Steel (1.08% C) | 10.8 | 6.0 | ||||||||
| Iron Alloys | Steel (0.56% C) | 11.0 | 6.1 | ||||||||
| Iron Alloys | Steel (0.40% C) | 11.3 | 6.3 | ||||||||
| Nickel Alloys | Hastelloy C | 11.3 | 6.3 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Beryllium | 11.3 | 6.3 | ||||||||
| Nickel Alloys | Inconel | 11.5 | 6.4 | ||||||||
| Iron Alloys | Steel (0.06% C) | 11.7 | 6.5 | ||||||||
| Iron Alloys | Steel (0.22% C) | 11.7 | 6.5 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Iron | 11.8 | 6.6 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Palladium | 11.8 | 6.6 | ||||||||
| Iron Alloys | Cast Iron - Nodular | 11.9 | 6.6 | ||||||||
| Iron Alloys | Malleable Iron (pearlitic) | 12.0 | 6.7 | ||||||||
| Nickel Alloys | Monel (cast) | 12.9 | 7.2 | ||||||||
| Nickel Alloys | Ni-o-nel | 12.9 | 7.2 | ||||||||
| Nickel Alloys | Duranickel | 13.0 | 7.2 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Cobalt | 13.0 | 7.2 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Nickel | 13.4 | 7.4 | ||||||||
| Nickel Alloys | Monel | 14.0 | 7.8 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Gold | 14.2 | 7.9 | ||||||||
| Nickel Alloys | 35Ni-45Fe-20Cr | 15.8 | 8.8 | ||||||||
| Copper Alloys | Cupro-nickel, 305 | 16.2 | 9.0 | ||||||||
| Copper Alloys | Nickel silver, 65-18 | 16.2 | 9.0 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Copper | 16.5 | 9.2 | ||||||||
| Nickel Alloys | 60Ni-24Fe-16Cr | 17.0 | 9.4 | ||||||||
| Nickel Alloys | 80Ni-20Cr | 17.3 | 9.6 | ||||||||
| Stainless Steel | Stainless Steel type 304 | 17.3 | 9.6 | ||||||||
| Copper Alloys | Phosphor bronze, 1.25% | 17.8 | 9.9 | ||||||||
| Copper Alloys | Beryllium Copper | 17.8 | 9.9 | ||||||||
| Copper Alloys | Aluminum-Silicon Bronze | 18.0 | 10.0 | ||||||||
| Copper Alloys | Commercial Bronze, 90% | 18.4 | 10.2 | ||||||||
| Copper Alloys | Red brass, 85% | 18.7 | 10.4 | ||||||||
| Nickel Alloys | Constantan | 18.8 | 10.4 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Silver | 18.9 | 10.5 | ||||||||
| Copper Alloys | Low brass, 80% | 19.1 | 10.6 | ||||||||
| Lead Alloys | Lead-base babbitt (SAE 14) | 19.6 | 10.9 | ||||||||
| Copper Alloys | Inhibited admiralty | 20.2 | 11.2 | ||||||||
| Copper Alloys | Yellow Brass | 20.3 | 11.3 | ||||||||
| Copper Alloys | Muntz metal | 20.8 | 11.6 | ||||||||
| Copper Alloys | Naval Brass | 21.2 | 11.8 | ||||||||
| Lead Alloys | Solder (70Sn-30Pb) | 21.6 | 12.0 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Manganese | 21.7 | 12.1 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Tin | 22.0 | 12.2 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Calcium | 22.3 | 12.4 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Aluminum | 23.1 | 12.8 | ||||||||
| Lead Alloys | Lead-base babbitt (Alloy 8) | 24.0 | 13.3 | ||||||||
| Lead Alloys | Solder (63Sn-37Pb) | 24.7 | 13.7 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Magnesium | 24.8 | 13.8 | ||||||||
| Lead Alloys | Hard lead (94Pb-6Sb) | 27.2 | 15.1 | ||||||||
| Lead Alloys | 5-95 Solder | 28.7 | 15.9 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Lead | 28.9 | 16.1 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Zinc | 30.2 | 16.8 | ||||||||
| Pure Metals | Cadmium | 30.8 | 17.1 | ||||||||
The data used to create this Coefficient of Thermal Expansion table was compiled and adapted using information from various sources, including the following...
- Concise Metals Engineering Handbook
- Handbook of Chemistry and Physics - 91st Edition
- ASM Handbook Volume 1 - Properties and Selection: Irons, Steels, and High-Performance Alloys